Mechanisms Of Antibiotic Susceptibility And Resistance
Penicillin inhibits the replication ofS. pneumoniae by binding one or more enzymes needed to synthesize peptidoglycan, including higher-molecular-weight transpeptidases and a lower-molecular-weight carboxypeptidase, resulting in bacterial autolysis. The binding is covalent, and a serine esterlinked, enzymatically inactive penicilloyl complex is formed. Six peptidoglycan synthesis enzymes, which are also called penicillin-binding proteins , have been identified . Resistant isolates are characterized when penicillin shows decreased affinity for one or more of these enzymes due to mutations in the genes that encode them.264 Alterations in PBP2b are more likely to account for low-level resistance, whereas mutations in PBP2x have been associated with high-level resistance.265 Alterations in PBP2x and 1a also render pneumococci more resistant to third-generation cephalosporins, such as cefotaxime or ceftriaxone.266
Samantha J. Balboa, Leslie M. Hicks, in, 2022
Drug Resistance In Viruses
Antiviral drug resistance is an increasing concern in immunocompromised patient populations, where ongoing viral replication and prolonged drug exposure lead to the selection of resistant strains. Resistance has developed to most antivirals including antiretroviral drugs.
All antiretroviral drugs, including newer classes, are at risk of becoming partly or fully inactive because of the emergence of drug-resistant HIV . People receiving antiretroviral therapy can acquire HIVDR, and people can also be infected with HIV that is already drug resistant. Levels of pretreatment HIVDR to non-nucleoside reverse-transcriptase inhibitors among adults initiating first-line therapy exceeded 10% in the majority of the monitored countries in Africa, Asia and Latin America. The prevalence of PDR among infants is alarmingly high. In sub-Saharan Africa, over 50% of the infants newly diagnosed with HIV carry a virus that is resistant to NNRTI. Informed by these findings, latest WHO ARV guidelines now recommend the adoption of a new drug, dolutegravir, as the preferred first-line treatment for adults and children. The use of this drug is particularly urgent in averting the negative effects of resistance to NNRTIs.
What Can Be Done To Fight Antibiotic Resistance
Avoid using antibiotics for the treatment of viral infections,including colds.
How to fight back against antibiotic resistance?
To help fight antibiotic resistance and protect yourself against infection: Dont take antibiotics unless youre certain you need them. An estimated 30% of the millions of prescriptions written each year are not needed. Finish your pills. Take your entire prescription exactly as directed. Get vaccinated. Immunizations can protect you against some diseases that are treated with antibiotics. Stay safe in the hospital.
Also Check: What Antibiotics Cancel Out Nexplanon
Causes Of Antibiotics Resistance
Antibiotic resistance is caused by:
- overuse of antibiotics – the more times a bacteria comes in to contact with an antibiotic the more likely it is that the bacteria will find ways to change itself and survive
- bacteria growing, changing and spreading very fast – this means some antibiotics will no longer work properly for certain infections
- antibiotics killing our ‘good’ bacteria as well as our ‘bad’ bacteria – this means superbugs can grow and take over
How Can I Improve Antibiotic Use

No one can completely avoid getting an infection, but there are additional steps you can take to protect yourself and your family.
Taking antibiotics only when they are needed is an important way you can protect yourself and your family from antimicrobial resistance. Talk to your doctor about the best treatment if you are sick. Never pressure your doctor to prescribe an antibiotic.
When antibiotics arent needed, they wont help you, and their side effects could still cause harm. Ask your doctor or pharmacist about steps you can take to feel better when an antibiotic isnt needed.
If your doctor decides an antibiotic is the best treatment when you are sick:
- Take the medication exactly as your doctor tells you.
- Do not share your medication with others.
- Do not save them for later. Talk to your pharmacist about safely discarding leftover medicines.
- Do not take antibiotics prescribed for someone else. This may delay the best treatment for you, make you even sicker, or cause side effects.
- Talk with your doctor and pharmacist if you have any questions about your antibiotics prescribed to you.
Recommended Reading: Antibiotics Not Working For Tooth Pain
How Does Antibiotic Resistance Happen
Bacteria can become resistant to antibiotics in several ways.
- Some bacteria can change their outer structure so the antibiotic has no way to attach to the bacteria it is intended to kill.
- Some bacteria can neutralise an antibiotic by changing it in a way that makes it ineffective.
- Others have mechanisms that pump an antibiotic back outside of the bacteria before it can work.
- Bacteria can also become resistant through mutation of their genetic material. After being exposed to antibiotics, sometimes bacteria can survive by finding a way to resist the antibiotic. If even one bacterium becomes resistant to an antibiotic, it can then multiply and replace all the bacteria that were killed off.
Image credit: PHARMAC, NZ
The spread of antibiotic resistance occurs when resistant strains of bacteria are passed from person to person and from non-human sources in the environment, including food.
Management In Animal Use
Europe
In 1997, European Union health ministers voted to ban avoparcin and four additional antibiotics used to promote animal growth in 1999. In 2006 a ban on the use of antibiotics in European feed, with the exception of two antibiotics in poultry feeds, became effective. In Scandinavia, there is evidence that the ban has led to a lower prevalence of antibiotic resistance in animal bacterial populations. As of 2004, several European countries established a decline of antimicrobial resistance in humans through limiting the use of antimicrobials in agriculture and food industries without jeopardizing animal health or economic cost.
United States
Recommended Reading: Can Antibiotics Cause Blood In Stool In Dogs
Antibiotic Resistance In Healthcare
A significant factor in the increase of antibiotic resistance is people not being given a high enough dose of antibiotics to clear an infection or not completing the full course of antibiotics. The ‘weaker’ bacteria will be killed, but the stronger bacteria that can survive a low dose of antibiotic are left behind. These bacteria can then multiply, creating a new infection made entirely of stronger drug-resistant bacteria.
However, over-use of antibiotics is also just as significant a problem. If antibiotics are used when they’re not needed, to prevent an infection, treat a very mild infection, or where an infection isn’t caused by bacteria, drug-resistant bacteria are given an opportunity to thrive and multiply.
How Common Is Antimicrobial Resistance
According to the Centers for Disease Control , at least two million people per year in the United States become infected with resistant germs. At least 23,000 people die as a result. Each year, conditions caused by antimicrobial resistance lead to:
- An estimated $20 billion in additional healthcare costs.
- $35 billion in other costs to society as a whole.
- More than eight million additional days of hospital care.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Best Antibiotic For Bronchitis
Do Pets Get Infections That Need To Be Treated With Antibiotics
Yes. Pets can get infections just like people, and sometimes they are resistant to antibiotics typically used to treat them. As in health care, using antibiotics appropriately in veterinary medicine is important to prevent resistant infections.
Tripartite Joint Secretariat On Antimicrobial Resistance
The political declaration at the UN High Level Meeting on AMR, committed to by Heads of State at the United Nations General Assembly in New York in September 2016, confirmed a strong focus on a broad, coordinated approach that engages all including the human, animal, plant and environmental health sectors. WHO is working closely with FAO and OIE in a One Health approach to promote best practices to reduce the levels of AMR and slow its development.
The Interagency Coordination Group on AMR was convened by the Secretary-General of the United Nations after the UN High-Level Meeting on Antimicrobial Resistance in 2016. The IACG brought together partners across the UN, international organizations and individuals with expertise across human, animal and plant health, as well as the food, animal feed, trade, development and environment sectors, to formulate a plan for the fight against antimicrobial resistance. The Interagency Coordination Group on AMR submitted its report No time to wait: Securing the future from drug-resistant infections to the UN Secretary-General in April 2019. Its recommendations are now being implemented.
Recommended Reading: Best Antibiotic For Cut Infection
How Is Antimicrobial Resistance Diagnosed What Tests Are Done
Diagnostic laboratory tests can find which microbe is causing an infection and determine whether the microbes present are resistant to certain antimicrobial medications. However, these tests can take days or even weeks. This is because microbes must grow in a laboratory before they can be identified.
Information About Antimicrobial Resistance

If we are to protect ourselves against antimicrobial resistance, we need to know how often and where resistant bacteria occur, and if there are any trends in this regard. The National Institute for Public Health and the Environment systematically collects and analyses such information. We call this surveillance. This allows RIVM to track the use of antibiotics and the number of infections involving resistant bacteria in the Netherlands. For example, various laboratories help us by providing information about hospital patients and nursing home residents. Based on this information, we can see how often antimicrobials are being used, which bacteria occur where, whether the number of such cases is increasing or decreasing, and whether new bacteria are appearing. .
Don’t Miss: Can Antibiotics Help An Abscessed Tooth
Interagency Coordination Group On Antimicrobial Resistance
The United Nations Secretary-General has established IACG to improve coordination between international organizations and to ensure effective global action against this threat to health security. The IACG is co-chaired by the UN Deputy Secretary-General and the Director General of WHO and comprises high level representatives of relevant UN agencies, other international organizations, and individual experts across different sectors.
Can Hand Sanitizer Help Fix The Problem Of Antibiotic Resistance
Yes. Although antibiotic resistance is a big challenge with many contributing causes, infection prevention is an important part of the solution. Keeping hands clean, including with hand sanitizer, is an important way to prevent infections in individual people. We will use less antibiotics and have less antibiotic resistance if people do not get sick in the first place!
Recommended Reading: How To Heal Strep Without Antibiotics
How Did Mrsa Become Resistant To Antibiotics
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus is an infection with staphylococcus bacteria, commonly known as a staph infection, that cant be treated with many common antibiotics. MRSA was first reported in 1960, only a year after the antibiotic methicillin was introduced. But MRSA infections rose sharply in the early 2000s.
There are two types of MRSA infections. Those gotten in a hospital, and those gotten elsewhere in the community. Because this bacteria is especially contagious and hard to kill,
How Antibiotic Resistance Can Be Prevented
There is much work to be done at the macro level to combat the issue of antibiotic resistance, including the implementation of best practices in livestock care and stewardship initiatives in clinical care. However, Price said that there are also actions individuals can take to help the cause and promote personal health.
I think that we need to become better consumers of antibiotics, both in terms of the food products that we buy and how we approach medicine, Price said. We all have to lead this antibiotic stewardship movement in terms of how we behave as patients, as clinicians and as consumers.
Also Check: Antibiotic Drops For Corneal Abrasion
Global Antibiotic Research And Development Partnership
A joint initiative of WHO and Drugs for Neglected Diseases initiative , GARDP encourages research and development through public-private partnerships. By 2023, the partnership aims to develop and deliver up to four new treatments, through improvement of existing antibiotics and acceleration of the entry of new antibiotic drugs.
How Does Antimicrobial Resistance Happen
A microbe has five goals once it enters your body:
- To reach the target site .
- To attach to the target site.
- To take nutrients from you, the host.
- To avoid and/or survive any attacks by your immune system.
When you take an antimicrobial, the medication kills most of the microbes. But resistant microbes may survive.
You May Like: Antibiotics For Reptile Respiratory Infection
The Use Of Ceo2 For Detection Of Drug Resistance
Antimicrobial resistance is increasing at an alarming rate. The early detection of antimicrobial resistance is the basic requirement for better treatment strategies. Noll42 reported that CeO2 nanoparticles may play a pivotal role in detecting drug resistivity due to their ability to exist in a mixed-valence state and act as either oxidizing agents or reducing agents. The paper reported that the use of CeO2 NPs for detection of glucose concentrations was useful for the detection of an inhibitory versus noninhibitory concentration of the antibiotic ampicillin on both E. coli and S. aureus. Interestingly, in this technique, only a spectrophotometer is required for detection. Moreover, the method is simple and does not require acidic pH or other chemicals.
Ali Alawieh, … Fadi A. Zaraket, in, 2019
A Guide To Antibiotic Resistance
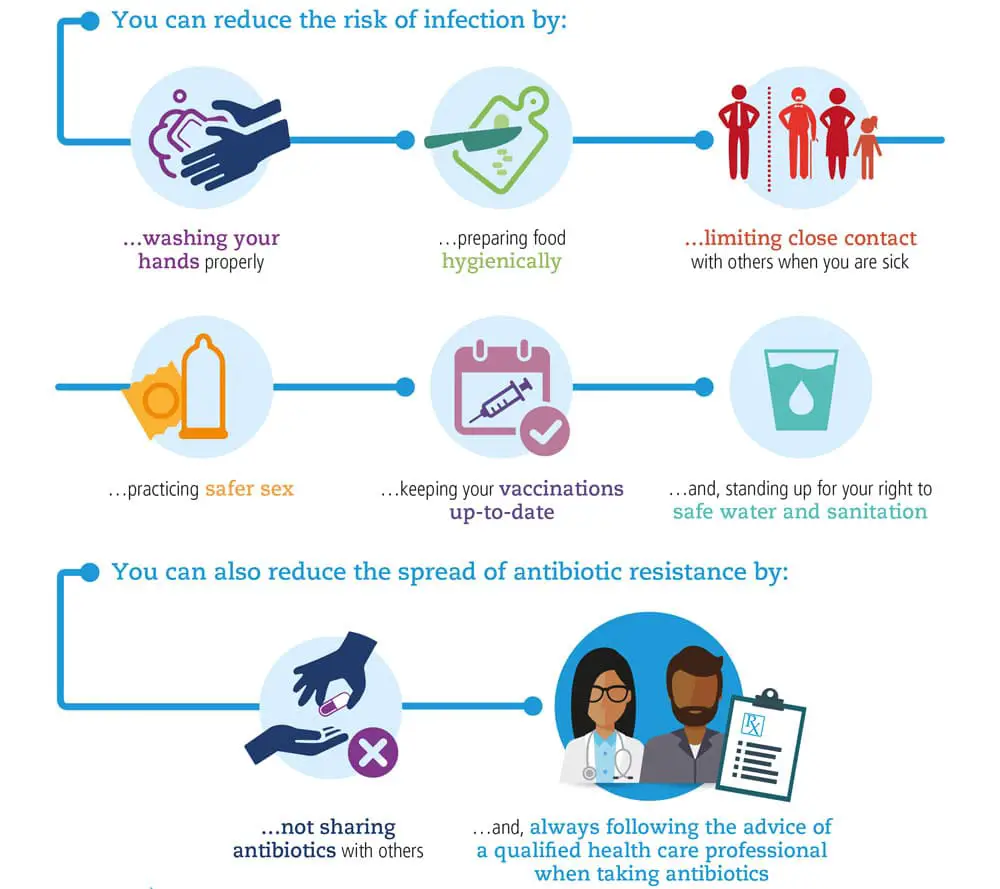
Antibiotics are a powerful tool in fighting infectious diseases. However, the overuse of antibiotics can lead to antibiotic-resistant superbugs, leaving the public vulnerable to infections that were once easy to cure and possibly resulting in death. According to the Antibiotic Resistance Action Center at the George Washington Universitys Milken Institute School of Public Health, without changes to how antibiotics are currently being utilized, the mortality rate for antibiotic-resistant infections will continue to grow.
There are many components to antibiotic stewardship that can reduce the occurrence of antibiotic resistance. Areas of focus can include antibiotic overuse in clinical medicine, pharmaceutical development of new antibiotics and the antibiotic misuse in livestock raised for food production.
Also Check: How Was Chlamydia Treated Before Antibiotics
Burden Of Antibiotic Resistance
Antibiotics have made many other medical advances possible, including transplants and cancer treatments. If antibiotics lose their effectiveness, we lose the ability to treat many diseases and perform many routine surgeries.
More than 1 out of 4 antibiotics prescribed in US outpatient settings are unnecessary. According to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , antibiotic resistance threatens everyone.
- Each year in the US, more than 2.8 million infections occur from antibiotic-resistant bacteria, and more than 35,000 people die as a result.
- In the US each year, antibiotic resistance adds $20 billion in excess direct health care costs. Additional costs to society for lost productivity could be as high as $35 billion a year.
- Hospital costs for a patient with an antibiotic-resistant infection can range from $18,500 to $29,000, depending on the type of infection.
Antimicrobial resistance can be costly and devastating for patients and families. Drug-resistant infections can lead to extended hospital stays, additional follow-up doctor visits, and the use of treatments that may be costly and potentially toxic.
What Do You Need To Know About Antibiotic Resistance
What do I need to know about antibiotic resistance? Antibiotics do not always kill all the bacteria causing an infection. Bacteria that survive will be stronger and may become resistant to antibiotics. Antibiotic resistance can happen when antibiotics are overused or not taken correctly. Antibiotic resistance makes infections hard to treat.
Also Check: What Antibiotics Treat Whooping Cough
Additional Precautions With Antibiotic Resistant Bacteria
Additional precautions are used when caring for people who are known or suspected to be infected or colonised with highly infectious pathogens .Micro-organisms may be classed as high risk if:
- their transmission route makes them more contagious they may be spread through contact or droplets, or may be airborne
- they are caused by antibiotic resistant bacteria
- they are resistant to standard sterilisation procedures.
Additional precautions are tailored to the particular pathogen and route of transmission. Additional precautions may include:
- use of a single room with ensuite facilities or a dedicated toilet
- dedicated care equipment for that person
- restricted movement of the person and their healthcare workers.
What Individuals Can Do
You can help, too. Experts recommend that people follow instructions carefully when a doctor prescribes an antibiotic for them. They also urge people to follow these guidelines:
- Do not demand antibiotics from your doctor or healthcare professional if they dont prescribe one for you, since antibiotics are only appropriate for bacterial infections.
- Do not take an antibiotic unless prescribed by a healthcare professional.
WHO , Antibiotic resistance is rising to dangerously high levels in all parts of the world.
Its not just antibiotic-resistant bacteria thats a concern. Bacteria are just one of several types of organisms that can become antimicrobial resistant. Viruses, fungi, and parasites can also respond to treatments by changing and becoming resistant.
According to WHO, they are all a growing global threat because this resistance leaves society with infections that become increasingly difficult or impossible to treat.
In fact, a 2022 systematic analysis of antimicrobial resistance estimated that 4.95 million deaths in 204 countries and territories were associated with bacterial antimicrobial resistance, and 1.27 million deaths were attributable to bacterial AMR.
The cautions that urgent action is necessary to avoid creating a post-antibiotic era. The WHO notes that there must be ongoing research into new treatments and better surveillance of antibiotic-resistant infections.
Scientists are investigating other types of potential treatments, too.
Also Check: Antibiotic Ointment For Diaper Rash
What Does Antibiotic Resistance Mean For You Your Whnau And The Community
Antibiotic resistance is a major concern because it means some infections will become more difficult, and sometimes impossible, to treat. If you or someone in your family develop an antibiotic-resistant infection:
- you may have the infection for longer
- you may be more likely to have complications from the infection
- you could remain infectious for longer and pass your infection to other people.
Infections caused by antibiotic-resistant bacteria are harder to treat, usually last longer, often result in longer stays in hospital and are associated with more complications. In serious cases they can cause death. Doctors have to use to less conventional antibiotics or a combination of different antibiotics to treat these infections. These are usually more costly and can have more-serious side effects. In Aotearoa New Zealand, the occurrence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria is increasing. Examples of antibiotic-resistant bacteria include:
- Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus a group of bacteria that are resistant to commonly used penicillin-like antibiotics
- Extended spectrum beta-lactamases chemicals produced by some bacteria that prevent certain antibiotics from working.
- Vancomycin-resistant enterococci a group of bacteria that are resistant to the antibiotic vancomycin.