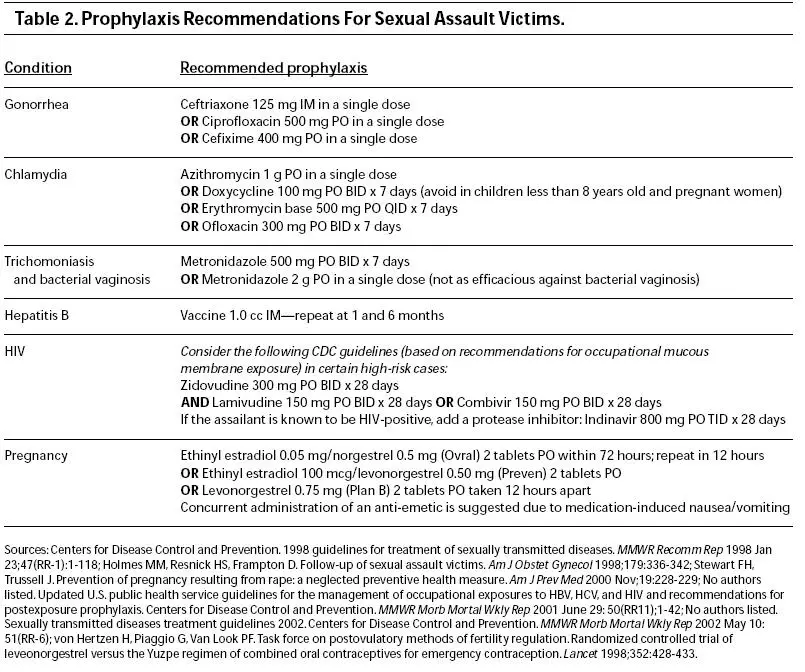
What Are Antibiotics And How Are They Used
Antibiotics are powerful drugs that are used to fight infections. Your healthcare team thinks you or your loved one might have an infection that can be treated with an antibiotic.
Not all infections are treated with antibiotics. While antibiotics may be effective against infections caused by bacteria , they are not effective against viruses.
Like all drugs, antibiotics can have side effects and should be used only when necessary. Taking an antibiotic you dont need can even be harmful. Because of this, there are important things to know about antibiotics.
Common Med Provides A Cheap And Effective Treatment
A clinical trial involving HIV-positive children in sub-Saharan Africa has revealed that a common antibiotic significantly improves health despite widespread antibiotic resistance.
In a paper in the journal Science Translational Medicine, researchers led by Claire Bourke from the Queen Mary University of London in the UK detail a trial involving 293 children in Zimbabwe and Uganda.
The children were all given the antibiotic cotrimoxazole for a minimum of 96 weeks.
The antibiotic has long been recognised for its prophylactic effect in people with HIV and AIDS, and is recommended by the World Health Organisation as an affordable, safe and feasible intervention for resource-limited countries dealing with HIV cases.
In the latest investigation to drill down into the effects of the medication, Bourke and colleagues studied plasma samples taken from the Ugandan and Zimbabwean cohort. After 96 weeks, treatment was halted for half of the children, and continued for the remainder.
The researchers found that those who continued treatment had lower rates of systemic inflammation and lower streptococcal bacterial activity than those who stopped. The latter group, also recorded an 18% higher risk of adverse health events, such as pneumonia, within 48 weeks of ceasing the antibiotics.
Cotrimoxazole was found to exert direct effects on the childrens immune cells. A small secondary trial found that the antibiotic also reduced inflammatory molecule production in HIV-positive adults.
Do You Need To Keep Taking Hiv Treatment
Yes. ART is not a cure and the virus remains in your body, even when your viral load is undetectable, so you need to keep taking your HIV medicine as prescribed. If you stop taking your HIV medicine, your viral load will quickly go back up.
If you have stopped taking your HIV medicine or are having trouble taking all the doses as prescribed, talk to your health care provider as soon as possible. Your provider can help you get back on track and discuss the best strategies to prevent transmitting HIV to your sexual partners until your viral load is confirmed to be undetectable again.
Get tips on taking your HIV medicine as prescribed.
Read Also: When You Need Antibiotics For Sinus Infection
Study Site And Population
The study was conducted in urban and peri-urban areas of Maputo and Matola cities, located in Southern Mozambique covering an area of 300 km2 and 367 km2 . In 2013, there were in total 35 primary level health facilities in both the cities. Primary health care is the first level of healthcare and is characterised by a set of health actions, at the individual and collective level, which covers health promotion and protection, disease prevention, diagnosis, treatment, rehabilitation, harm reduction, and health maintenance. We selected in total eight primary care HFs according to established criteria, which included the existence of prescribers in the screening and consultation rooms, attendance of more than 600 HIV patients per month, and a pharmacy dispensing medication to HIV patients. All selected HFs had antiretroviral therapy service, patient counselling service, and voluntary testing service, and appropriate follow-up.
The primary care for HIV-positive people in the study area is provided by general practitioners, medical technicians, and nurses. All HIV-positive patients of all ages who presented consecutively at HF medical visit with a complaint were included in the study, based on the following inclusion criteria: HIV-positive patient in follow-up or diagnosed on the same day of consultation, absence of severe pathology that would interfere with the ability to consent and accepting freely to sign the consent.
Effects On The Immune System
HIV primarily affects the body by targeting and damaging cells in the immune system. The immune system protects the body against viruses, bacteria, and fungi.
After attaching itself to a type of white blood cell called a CD4 T cell, the virus merges with it. These T cells are an important part of the immune system.
Once inside the CD4 T cell, the virus multiplies. It damages or destroys the cell, then moves on and targets other cells.
A persons CD4 T-cell count is an indication of the health of their immune system.
A healthy CD4 T-cell count is 5001,600 cells/mm3 of blood. If a person does not receive treatment for HIV, their CD4 T-cell count drops over time.
When it drops below 200 cells/mm3, the persons immune system is significantly impaired, making them more susceptible to opportunistic infections.
Recommended Reading: How To Fight Infection Without Antibiotics
Can Natural Herbal Or Alternative Medicines Cure Hiv
No. There is no natural, herbal or alternative cure for HIV. Antiretroviral treatment is the only medication that can control HIV. Taking herbal medicines can be dangerous as they will not protect your immune system from the damage caused by HIV. Some herbal medicines can also make antiretroviral treatment less effective.
Number Of Antibiotics Prescribed In Each Prescription
Among those patient visits with antibiotics prescribed, 48.2% received one antibiotic, 12.0% received two different kinds of antibiotics, 3.3% received three different kinds of antibiotics and 2.4% received four different kinds of antibiotics . Overall, the antibiotic combinations were 17.6%. In the antibiotic combinations, 69.4% were from two different classes, 24.2% of three classes, and 6.4% of four different classes . The association between penicillin and sulphonamide was the most frequent with 29.2%, followed by macrolide associated with quinolone and metronidazole .
Number of antibiotics prescribed in each prescription.
Don’t Miss: Who Makes Fish Aid Antibiotics
Gene Therapy Using Engineered Cd8+ Cells
Chimeric antigen receptors are engineered receptor proteins. They are called chimeric because they are a combination of two different proteins. In this case, an antigen-binding domain glued to the signaling domain of T cells. The signaling domain of T cells is what gives white blood cells the signal to release biochemical compounds that kill pathogens or infected/mutated cells. CAR-T therapies have been successfully used to treat some cancers.
In the case of HIV, researchers have engineered T cells or natural killer cells to express a chimeric receptor that can selectively bind and kill infected cells that express HIV envelope protein. An early example of these CAR-T cells expressed a receptor consisting of the extracellular domain of CD4 fused with the signaling domain of cytotoxic T cells. Since CD4 is the receptor that binds HIV envelope protein, any infected cells with Env on their surface should be recognized by this CAR-T cell. This would then trigger a signaling event that leads to the release of toxic particles, killing the HIV-infected cell. Disappointingly, however, researchers found that CAR-T cells expressing the chimeric CD-4 receptor can become infected with HIV, and these efforts failed to significantly cure patients of HIV in clinical trials.
Kuhlmann AS, Peterson CW, Kiem HP. Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell approaches to HIV cure. Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2018 13:446-453. doi:10.1097/COH.0000000000000485
How Is Hiv Treated
Although there is no cure for HIV, medications can dramatically slow the progression of the disease and people can live a relatively infection-free life. Few people die of AIDS these days thanks to effective treatments.Medications used to treat HIV are called antiretrovirals . Most people with HIV take combination ART every day. ART also reduces the risk of HIV transmission. Approved ARV treatments are grouped into seven drug classes as follows:
- Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors
- Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors
- Protease inhibitors
Recommended Reading: Can Any Antibiotics Cure Uti
Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors
These drugs interrupt the virus from duplicating, which may slow the spread of HIV in the body. They include:
Combinations of NRTIs make it possible to take lower doses and maintain effectiveness. These drugs include Combivir , Trizivir , Epzicom and Truvada . We expect more combination drugs to be available in the future.
When Not To Use Antibiotics
Antibiotics are not the correct choice for all infections. For example, most sore throats, cough and colds, flu, COVID or acute sinusitis are viral in origin and do not need an antibiotic. These viral infections are self-limiting, meaning that your own immune system will usually kick in and fight the virus off.
Using antibiotics for viral infections can increase the risk for antibiotic resistance. Antibiotic-resistant bacteria cannot be fully inhibited or killed by an antibiotic, even though the antibiotic may have worked effectively before the resistance occurred. This can also lower your options for effective treatments if an antibiotic is needed eventually due to a secondary infection. Using unnecessary antibiotics also puts you at risk for side effects and adds extra cost.
It’s important not to share your antibiotic or take medicine that was prescribed for someone else, and don’t save an antibiotic to use the next time you get sick. It may not be the right drug for your illness.
To better understand antibiotics, its best to break them down into common infections, common antibiotics, and the top antibiotic classes as listed in Drugs.com.
Also Check: Antibiotics Used To Treat Bacterial Vaginosis
When To Start Hiv Treatment
Its now recommended that everyone diagnosed with HIV starts treatment straight away after being diagnosed.
In the UK, national guidelines set out standards for HIV treatment. They currently recommend that anyone with HIV who is ready to commit to treatment should start it regardless of their CD4 count .
Will I Develop Resistance To Medication
If you skip doses of your HIV drugs regularly, you might develop resistance to the medicine, which means the medicine wont work on you as well as it should.
Your doctor can help lower your chance of resistance to HIV medicines by choosing effective medicines and by using a combination of medicines instead of just one. You can help lower your chances of developing resistance by taking each dose on time.
If you do develop resistance, your doctor may start you on different medicines, or recommend a combination of more than 3 medicines.
Tell your doctor if you are concerned about your symptoms never stop or change your medicine on your own.
Recommended Reading: Antibiotics That Start With C For Tooth Infection
Patients And Study Design
We conducted a retrospective cohort study of HIV-1infected patients with syphilis to investigate the efficacy and safety of oral amoxicillin plus probenecid for the treatment of syphilis at the AIDS Clinical Center, National Center for Global Health and Medicine , Tokyo, Japan. The enrollment criteria were HIV-1infected patients who were diagnosed with syphilis and started treatment with 3 g oral amoxicillin plus probenecid at our center between January 2000 and June 2014. We included all patients treated with the combination of 3 g amoxicillin and probenecid, irrespective of the dose of the latter. The diagnosis of syphilis was based on both serum rapid plasma regain titers 8 and positive T. pallidum hemagglutination result . The following exclusion criteria were applied: lack of follow-up tests, patients with neurosyphilis diagnosed based on the findings of cerebrospinal fluid , or ocular or auditory syphilis, patients who started treatment with antibiotics other than 3 g amoxicillin plus probenecid, patients with clinical symptoms compatible with primary or secondary syphilis but RPR titers < 8, patients suspected of reinfection after initiation of syphilis treatment .
What Questions Should Be Asked About Treatment With Antibiotics
It is important to understand what is happening with you or your loved ones care. Here are a few important questions caregivers or patients should ask about antibiotic treatment:
- What infection is this antibiotic treating? How does the healthcare team know that is the infection?
- What side effects might occur from this antibiotic?
- How long should these antibiotics be taken?
- Are there special instructions on taking this antibiotic, such as which medications or supplements are safe to take with it, or if it should be taken with food?
- What tests or monitoring will be done during treatment to show that the antibiotic is working?
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 11/20/2016.
References
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention – Get Smart: Know When Antibiotics Work. Antibiotic Resistance Q and A
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention – Get Smart: Know When Antibiotics Work. What Everyone Should Know
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services.Policy
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services.Policy
You May Like: Where To Get Antibiotics For Cats
Why Is It So Hard To Find A Cure For Hiv
Due to the complex nature and structure of HIV, locating and quantifying the amount of virus in the body is very difficult.
HIV evades the immune system by staying dormant in infected T-cells until they are activated to respond to infections. This state is called latent infection. Some of these cells may live for decades without becoming activated. Cells that are latently infected are described as the `HIV reservoir`.
Detecting and eliminating these cells are the biggest challenges facing cure research.
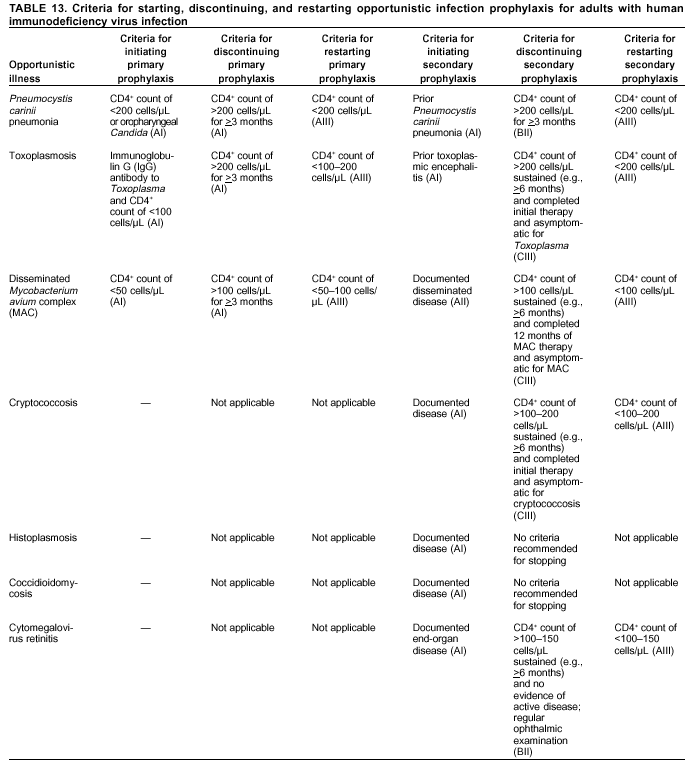
Acquired Hiv Drug Resistance
Viral load suppression the goal of HIV treatment is the prevention of HIV drug resistance. When viral load suppression is achieved and maintained, drug-resistant HIV is less likely to emerge. In 14 nationally representative surveys implemented between 2015 and 2020, the level of viral load suppression among adults receiving ART was generally high. The pooled results for viral load suppression in Africa were 94% among adults receiving first-line ART and 84% among adults receiving second-line ART. In the Americas, the pooled results for viral load suppression were 81% among adults receiving first-line ART and 70% among adults receiving second-line ART.
Despite treatment with potent medicines and even when adherence to treatment is supported, some HIV drug resistance is expected to emerge. Surveillance of acquired HIV drug resistance in populations receiving ART provides valuable information for the optimal selection and management of ART regimens. Among populations failing NNRTIs-based ART, the levels of resistance to commonly used NNRTIs ranged from 50% to 97%.
The high levels of HIV drug resistance to NNRTIs among individuals with treatment failure emphasize the need to scale up viral load testing and enhanced adherence counselling, and to promptly switch individuals with treatment failure.
You May Like: Broad Spectrum Antibiotics Over The Counter
Researchers Have Discovered An Unexpected Potential Weapon Against Hiv Protein
- Date:
- Michigan Medicine – University of Michigan
- Summary:
- A class of antibiotic molecules called pleicomacrolides inhibit the Nef protein, which HIV uses to evade the body’s immune system.
Ever since the first cases of a mysterious disease in the early 1980s exploded into the HIV/AIDS pandemic, researchers have been searching for ways to outsmart the deadly virus. Now thanks to anti-retroviral therapy, people living with HIV can live relatively normal lifespans — as long as they take their medications every day.
“If they ever stop, in short order the virus rebounds and resets at the high levels seen before starting — and that seems to be the case even after decades of therapy,” says Mark Painter, Ph.D., a graduate student in the University of Michigan Medical School’s department of microbiology and immunology.
The reason is that HIV can hide inside the human genome, lying dormant and ready to emerge at any time. Because of this, a true cure for HIV relies on waking the latent virus and eliminating it before it has a chance to again take hold of the body’s cells, an approach known as shock and kill.
The research tried determine if there was an FDA-approved drug or molecule already on the market that could override Nef, restore the functioning of MHC-I and allow the body’s own immune system, specifically cells known as cytotoxic T lymphocytes, to recognize the HIV-infected cells and destroy them.
What Is The Treatment For People With Syphilis And Hiv
As with diagnosis, the treatment of syphilis in HIV-positive people is similar to that for HIV-negative people.
Treatment of the early stages of syphilis typically involves a single injection of the antibiotic penicillin. Later stages of syphilis can involve additional injections or a course of intravenous antibiotics.
Because having HIV is associated with the potential risk of ineffective syphilis treatment, careful follow-up is important. This typically involves repeat syphilis blood tests in the months after treatment to verify that treatment was effective.
Recommended Reading: What Can You Take In Place Of Antibiotics
Having Syphilis Makes It Easier To Contract Hiv
If someone is HIV-negative, having syphilis can make it easier to contract HIV. This is because sores or inflammation due to syphilis can make it easier for HIV to enter the body.
A 2020 meta-analysis evaluated 22 studies involving a total of 65,232 participants. It found that HIV incidence doubled in people with syphilis compared to those without syphilis.
This association may also work the other way around. A of 4,907 HIV-positive individuals found that repeat syphilis infections increased over 11 years of follow-up. Factors associated with repeat syphilis in this study included:
- being assigned male at birth
- having a previous history of STIs
Both syphilis and HIV share risk factors when it comes to sex, such as having sex without a condom or having many sexual partners.
What Should I Know About Antibiotic Safety

Antibiotics are powerful drugs that are generally safe. They are very helpful in fighting disease, but sometimes antibiotics can actually be harmful.Key facts to know about antibiotic safety:
- Antibiotics can have side effects including allergic reactions and serious, possibly life-threatening diarrhea caused by the bacteria Clostridium difficile . Antibiotics may also interfere with other drugs you may be taking.
- Side effects of antibiotics are responsible for almost one out of five emergency department visits. They are the most common cause of emergency department visits for children under 18 years of age.
- When you take an antibiotic you do not need, you are unnecessarily exposed to the side effects of the drug and do not get any benefit from it.
Taking an antibiotic you dont need can lead to the development of antibiotic resistance. When resistance develops, antibiotics may not be able to stop future infections. Every time you take an antibiotic you dont need, you increase your risk of developing a resistant infection in the future.The bottom line: antibiotics come with benefits and risks. If you are prescribed an antibiotic, discuss the balance of benefits and risks with your healthcare team.
You May Like: Buy Antibiotics Online No Prescription